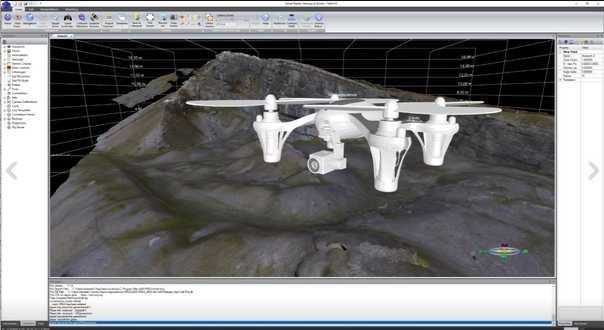
Designed and developed by geologists.
VRGS is the most powerful digital outcrop modelling software available.
Find out about VRGS's extensive features below
Your Digital and Virtual Outcrop Modelling Solution Is Here
Find out more details about VRGS's extensive and continually developing features below:
Import and export
Load data from multiple formats
Import data from obj, ply, slpk, DEM, ASPRS las, GeoTIFF and a variety of other formats. Interpretation export is supported by a flexible spreadsheet-based view, .csv and .dat files, or through other standard formats.
Need data exported in a particular format? Contact Us and we will see what we can do.
Interpretation
Make interpretation easier with the right tools for the job
You can map bedding, faults and fracture attitudes using the orientation tool. Use polylines for mapping beds, fault planes and key stratal surfaces. Geo-polygons are used to map geobodies such as channels and get corrected width thickness measurements.
More about interpretation tools

Annotation
Bring an extra level of clarity to your datasets with additional information
Add descriptions and annotations using billboards, projective images, waypoints, scale bars, multimedia objects and sketch layers.
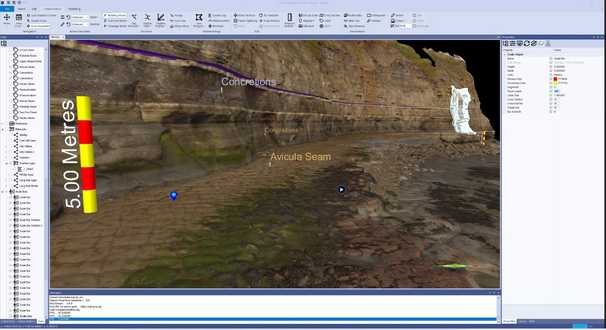
Georeferencing
Merge your datasets into a unified coordinate reference system
Merging and georeferencing data from different sources can be tricky, but with the toolkit in VRGS you can merge your datasets into a unified framework. Transform between coordinate reference systems, re-position data using ground control points, or merge datasets together using the iterative closest point algorithm to minimise the error between datasets (ideal for merging outcrop models with DEM’s).
ortho panels
Create accurate true dip and strike oriented projections of your models
In an orthographic projection parallel lines remain parallel, as opposed to a perspective projection which has a vanishing point. Creating an ortho-panel projected along structural strike or dip allows you to create a corrected dip or strike view of your outcrop. This can often give you a clearer view of the geometry or architecture of the geology.
projective textures
Project image data onto your models
Projective textures allow you to re-project images or data back onto an outcrop model. You may wish to do this with an image of some seismic data to show how it relates to the outcrop. It can be a high-resolution image to enhance detail in the texture, or it can simply be some extra annotation or a scan of a sedimentary log.

cross sections
Add geological cross sections to show subsurface geometry
Add complex geological cross sections with multiple sections to your models. Import bitmap images into the cross sections to show seismic data or traditional geological sections. Once imported, sections can also be used to create interpretations such as polylines to link with the outcrop data.

stereonets
Analyse your structural data in real-time as you interpret
Stereonets allow us to visualise and analyse complex three-dimensional structural data in two dimensions. VRGS has two kinds of stereonet view, a real-time view which plots data as you are interpreting, and a more flexible stereonet view for more complex analysis. You can plot your data as poles or planes, view intensity contour maps and interactively select and group orientation sets from the stereonet. Orientation attributes from point clouds and meshes, as well as from orientations, can also be used for analysis and classification.
More about structural geology
Measured Sections
Integrate sedimentological or mineralogical descriptions with your outcrop data
Outcrop logs, or measured sections, allow detailed descriptions of sedimentology or mineralogy. Outcrop logs can be measured directly from your outcrop models, with accurately measured thickness information. DOMs can be used to plan field logging campaigns, and even provide templates to take into the field. Field logs can also be integrated into your outcrop model using the built-in log description tools. Logs can also be used as a rich source of geostatistical data for use in stochastic modelling systems.
More about measured sections

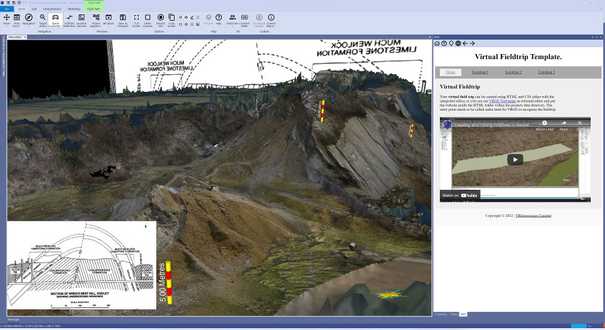
virtual field trips
Enhance real world field trips or visit otherwise inaccessible locations virtually
Virtual field trips can really improve the understanding of geology, either as stand-alone exercises or when combined with a real-world trip. Make your field training classes more effective by getting your group up to speed before the trip, or with a review session when back. Visit locations where you cannot take a group, or even locations you have never been to yourself. The virtual field trip also provides a good opportunity to reduce your carbon footprint.More about virtual field trips
VR and Desktop
Immerse yourself in digital outcrop data
VR allows the user to experience the dataset in its true scale, rather than just seeing it on the screen. The concept and understanding of scales of observation is of immense importance in geological training, and VR gives an effective way of doing this in the office. VR is also fantastic for quality control on digital outcrop datasets whose complex nature can often make it difficult to see errors on a 2D screen.

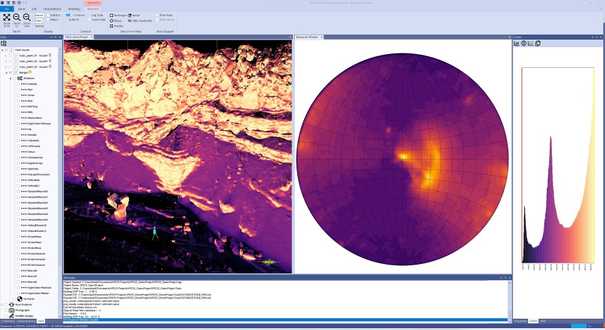
Attribute Analysis
Surface derived attributes for classification and interpretation
You can create a wide range of attributes from your point cloud and attribute datasets. Choose from radial basis functions, or K nearest neighbours. These attributes can be used as an aid for manual interpretation, or a basis for automated classification and mapping approaches.
Sketchfab Upload
Uploading your VRGS models to Sketchfab from within VRGS
VRGS can upload directly to Sketchfab, so you can share your models, interpretations and annotations. Simply connect VRGS to your Sketchfab account, prepare your scene and VRGS will upload your model for you.
Flight Paths
Record movies of your models and interpretations directly from within VRGS
A flight path is a route defined through a model via a series of key-frames. These flight paths can be used for creating videos from your outcrop models. Render your flight path to a movie file from within VRGS, and add your own branding if needed. A fantastic way of creating content for presentations or social media.
AI and ML
Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning for digital outcrops
The aim of artificial intelligence is to make the computer perform human tasks, in this case interpreting digital outcrop data. VRGS uses AI approaches such as Ant Colony Optimisation and density estimation trees to classify data.
This is an area of active development in VRGS, with new processes and techniques added in future updates.
Multiuser
Collaboration and training for geologists, geoscientists and engineers
With collaboration tools, training can be made more visually engaging, and oriented towards activities rather than passive viewing. Bring teams together for improved communication and collaboration, stimulate discussions, and enhance training through increased interaction.